If you have ever applied for a loan you may have found banks poring over your credit history and paying special attention to your credit scores.
Why won’t they?
Your credit score tells banks how likely you are to repay your loans. It's a measure of your trustworthiness. The world of email marketing isn’t too dissimilar.
The sender score is similar in that it analyzes your email sending history to track the kind of emails you send to your subscribers.
Your sender's reputation score is an aggregate value that comprises the number of spam complaints against you, the presence of your sending email id inside email blacklists, and more such things. You’re sending many kinds of emails like transactional emails, promotional emails, and more. The sender's reputation is your trump card that ensures that these emails you send are all delivered.
In this post, we’re going to talk about all the factors that affect the sender's reputation. How to build the sender's reputation, monitor it, and protect the same.
What is a Sender Reputation Score?
A sender reputation score is a number between 0 and 100 and shows your reputation as an email sender and is a signal regarding how the mailbox companies view you. The sender score is never constant. It’s dynamic and keeps changing. The higher the score, the easier it is going to be for your emails to land in the inbox of the receiver.
What do mailbox service providers look at to determine sender reputation?
- The quality of engagement from recipients. This can be arrived at by looking at the open rates, click rates, unsubscribe rates, and complaint rates
- Sending volume
- Quality of content in the emails sent
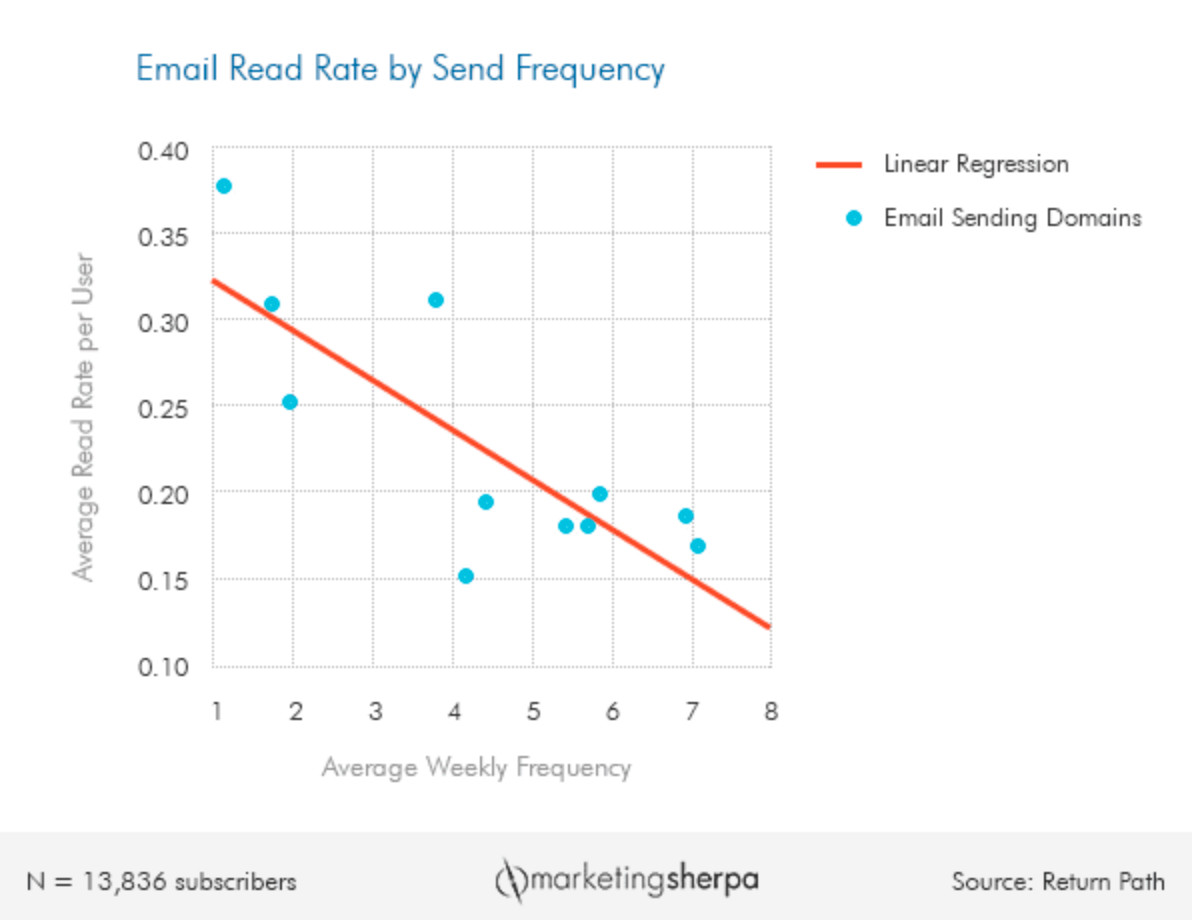
Return Path’s study showed email read rates decreased when email sending frequency increased.
Set expectations with new subscribers on the subscribe us page itself as to how many emails they can expect from you. This tells them how many days of the week they will see your email and it's best to stick to those limits.
Things like the frequency of mailing too can make a big impact on engagement.
These are a few of the examples of signals email provides when figuring out sender reputation.
Here are the most important things to keep in mind:
- If the sender's score is lower than 70, you need to work hard to improve your sender's reputation. You may need a dedicated IP for sending emails
- If above 70 that means your reputation is good. You need to keep an eye out so that the score doesn’t drop further
- If the score is above 80 you’re doing great and maybe entering a whitelist for sender score reputation
Here’s everything important for a good sender score:
- Domain Reputation
- IP Reputation
- Content Reputation
Domain Reputation
Domain Reputation is the strongest factor that influences the deliverability of mass emails. If you’re someone sending tons of cold emails, domain reputation can take you places. Domain reputation is far easier to track for email companies than running individual IPs and has by far the biggest impact on sender reputation.
Here are the influencing factors of domain reputation:
- DKIM signing domain: DKIM Domain is something you can see when looking at the full headers of the email. You view it under “Authentication-Results”.
- Return-path domain: This is used in the Return-path header of the email
- FROM domain: The domain used the from the address of the email you are sending
Different mailbox software companies use a range of factors to determine sender scores and give varying degrees of importance to different factors.
Of that, Gmail assigns the highest importance to domain reputation compared to any other mailbox.
IP Reputation
IP reputation is another determining factor and it looks at the reputation of the IPs for the emails you are sending.
Most mailboxes use domain reputation, but IP reputation is still quite important. Most mailbox companies look heavily at both IP and domain reputations to get a sense of the sender's reputation score and decide which emails they’re going to accept from you.
Content Reputation
What matters next is the actual content of the email. It also adds to the overall reputation and can make or break email deliverability. The domain and the IP reputations are measurable with the help of the postmaster tools that come with the mailboxes and the content reputation cannot be measured directly. However, it can be had with different tests on it.
Here is what helps track the reputation of the content.
- The links in the domains the image hosting domains
- The text phrases with HTML tags
- The text phrases in the content of the email
- Text phrases in the content of your email.
How to Build up your Sender Reputation
Now we know about all the different factors that influence the sender's score, let's look at all the different factors that play a role in improving your score.
Here are strategies that can improve your sender's reputation.
Metrics like the delivery of the open and click rates indicate sender reputation.
What data are you collecting?
As a sender, you may need to spare a hard look at the path a user may take for signing up for the service. For instance, an online logo maker site may need information on the client’s business name and its size.
Look at the email ids, third-party options, and app sign-ups. The sequences show the responses and their quality. When you segment the user base you can create a campaign for them.
When you segment the users you can create personalized campaigns.
Segment the data correctly
With data segmentation what you’re trying to do is group your users into lists based on where they are in their life cycle. The users can be grouped by fixed attributes, say their presence in a particular stage of the marketing lifecycle. Some of your subscribers will be open to receiving informational content. Others want coupons. Sending different content to different users based on what they are most likely to find useful helps ensure that the content they’re getting helps you produce higher engagement.
These are the questions to ask when you segment different users:
- The email the user gets on sign up
- The time the person spends reading the email
- The number of dormant emails
- Sending relevant emails on the lifecycle stage
Create targeted content
The filtering system for the mailbox providers breaks down the content inside the email into separate components and calculates the reputation of each component. If the sum of that calculation shows up in the negative then your emails are going to the spam box rather than the inbox.
How to monitor your sender's reputation?
These are the best practices for you to ensure that your sending reputation is constantly great.
Keep a close eye on statistics to understand trends
Sending reputation is simply putting together the number of emails that make it to the inbox of your audience. You need to see statistics like the lower open rates, higher rates of complaints, and more such factors that indicate the decline of the quality of your list.
On the flip side, if you see improving open rates or higher delivery, that implies your sender's reputation is on the rise. You need to track these things domain-by-domain to identify reputation issues granularly.
Properly authenticate the emails
The emails should be properly authenticated passing both SPF and DKIM parameters.
Minimize feedback loop complaints
The complaints arise when users mark your email as spam on email providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and Hotmail. The average rates of these should be less than 0.1% on these providers.
Monitor open and click rates
You should also measure the number of opens and clicks for the emails you’re sending. This is a measure of engagement.
Monitor unsubscribes and bounces
The total number of unsubscribes and the number of bounce ids and metrics need to be monitored.
Monitor the delivery speed
If your email service provider delivers 500k to 1000k emails an hour do you see any throttling? If there’s some throttling there may be something negative going on with your campaign. This affects performance, your deliverability, and more.
A great sender reputation is the number 1 way for you to ensure that your emails are getting delivered. Each email service provider has a different perspective on sender reputation. That’s why the factors that influence assessment can change a lot.
Keep an eye out for these metrics:
- The spam complaints
- The hard bounce rate
- Spam trap hits
Before making improvements to the content, test the changes and the frequency of your mailing by sending out the mailer to a small portion of the list. Then measure the complaint rate after you have sent this new email to the small segment of users.
If the new email results in higher complaint rates that implies you need to rethink your strategy.
Don’t change your IP address
Spammers routinely change their IP addresses. For permission-based sending, you need a new IP address, a new server, and a dedicated server for running tests.
The IP addresses that lack volume due to higher levels of traffic and mission throttling.
Look for IP deny problems
If your email generates several negative issues like delivery to honeypot email addresses you will see an increased rate of denial listing for your emails.
There are free tools that can help you with this.
Send messages to you
Most email service providers have a preview feature that lets you see how the email would look at the other end. If you have different email addresses at different providers like Gmail, Outlook, and more it’s a great idea to send each of these emails. This helps you understand if the emails are landing in your inbox or spam folders and can be a good indicator of how your spam reputation is faring.
At the same time, if these messages land in the spam folders, you can bring them back to the inbox and help your case.
Segment new opt-ins or risky test email
You should send a different set of emails to newly opted-in emails with a different server. This helps improve email deliverability.
Sort Unsubscribers after each campaign
Remove the number of opt-outs from the list. This minimizes the number of spam complaints. Test the unsubscribe process as part of regular audits. process before each sends to make sure that it still works.
Make sure to remember CAN-SPAM
The CAN spam regulations give you 10 days from the date of opting out to add the email id under the Do not email list. You can make use of email deliverability tools to do this.
Monitor hard bounces
Remove email addresses where you’re not able to deliver new emails because of the addresses being invalid.
Remove these hard bounces from the list before attempting to send them again. You can rescue these addresses with techniques like direct mail offering incentives to opt-in again.
Review and monitor DNS records
DNS is a simple thing. And yet it’s important. When working with different services, having several domains configured in several different ways, you can easily lose track of things.
If you don’t monitor SPF, DKIM, and DMARC configurations in your DNS that may mean that your emails don’t get delivered. You can monitor DNS records through the MX Toolbox or Mail Tester’s SPF and DKIM checking.
Monitor IP addresses
Ensure that your IPs are not on a spam blacklist. If you’re on a web host or email host that has you on shared IPs the delivery IP can be blacklisted simply because someone sharing the IP is blacklisted.
Keep an eye out for the IP and domain reputation which is one of the most important signals to ISPs. If your domain has a bad reputation it’s going to be difficult.
Many services can help with this. They monitor and check your IPs as there are 100 different blacklists.
To monitor IP addresses and the overall health of your email sending accounts here are some good tools I recommend:
MxToolbox
MxToolbox helps you monitor to make sure you have SPF, DKIM, and Reporting and Conformance protocols established.
MxToolbox provides information on these things:
- Who is sending email from your domain
- What’s the reputation of those IPs you are sending emails from
- Geolocation of senders
- You also get alerts to changes in email reputation
As a free user, you can monitor one domain with access to 30 blacklists. Paid users get unlimited monitors, blacklists, and delivery tools.
You also get a dedicated team for you to understand email blacklisting and what to do to improve email configuration in the future to improve delivery.
MailTester
MailTester is a different tool that analyzes your email message, its server, and its sending IP address. It then uses the information to generate a comprehensive report of what’s configured well. The result can be accessed for free for 7 days in the free version and 30 days with a paid plan.
If you do only a few tests you can access the web version for free without even creating an account.
Features provided under a paid plan:
- Integrate mail tester results in the application with JSON API
- While labeling the service and getting statistics about tests on daily weekly and monthly use
- No ads on the site
- No expiry on the tests purchases and the option to purchase more tests any time you want.
TrustedSource
TrustedSource gives information on the domain’s email reputation and reputation of the domain along with DNS and mail servers. It’s pretty comprehensive in its reporting.
Google Postmaster Tools
Google has Postmaster Tools that lets you track data on high-volume emails sent into Gmail. They have IP reputation, domain reputation, delivery errors, and more things.
Of the metrics it shows, the Gmail IP reputation and Domain reputation as the strongest factors for sending emails. With the IP reputation report, you see the general quality of the IP addresses you’re sending emails from. It’s a good signal to keep an eye on. The domain reputation is another factor. It shows you how Gmail views your domain. It can be BAD, LOW, MEDIUM, or HIGH.
FAQs on email deliverability
1) What is Email Deliverability?
Email deliverability determines if your email will go to the audience’s inbox.
2) What is SPF, and DKIM signatures?
SPF lets the sender define the IP addresses that can be used to send email from a particular domain. The DKIM gives you the encryption key and signature that verifies if the email message was altered.
3) What is a good email deliverability rate?
The average email deliverability stood at 80% in 2021. And anything above 80% is a good enough score.
Conclusion
Building a great email sender reputation is a challenge. The policies of ISPs and the makeup of your subscriber list are always changing and your reputation can always take the fall for not keeping up with those changes. It takes an eagle’s eye to constantly maintain the health of your list. What do you think of the strategies above? Do let us know in the comments below.
Email reputation is generally something you have a big deal of control over. With these tools and tactics, you can get better visibility into how mailbox providers see your email. The better you’re with the approach the better your deliverability is going to be.
With these tools that I listed you can understand the chances of your deliverability. You can combine these tools when testing deliverability. When you gather data and experience you can pick the best two. If you are new to this, treat this as a starter guide to help you understand and move around the world of email deliverability. It is hard and most people may feel like giving up. However, it isn’t that big of a problem if you focus on the basics and keep your head straight.






