To begin with, it is important to understand the concept of Grey-listing technology. Once we clearly understand it, we can explore methods to circumvent its restrictions.
What is Greylisting
Greylisting (Or graylisting) is a method of defending e-mail users against spam.
Any email from a sender that is not recognized by a mail transfer agent (MTA) using greylisting will "temporarily reject." If the mail is legitimate, after a delay, the originating server will try again and the email will be accepted if enough time has elapsed.
It is a new popular spam-fighting feature, similar to whitelisting and blacklisting. Each time a mailbox receives an email from an unknown contact (IP), that mail is rejected with a "try again later" message. This means that all mail gets delayed at least until the sender tries again. This is where spam messages fail because they are not RFC-compliant and will not be resent later.
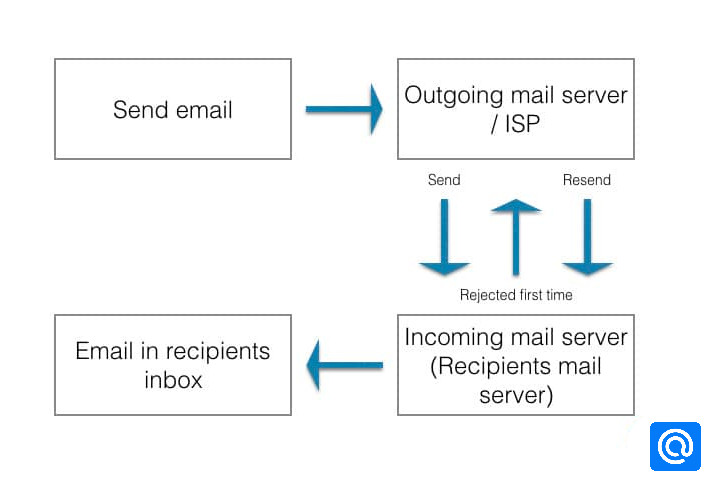
A mail transfer agent (MTA) using greylisting will "temporarily reject" any email from a sender it does not recognize. If the mail is legitimate, the originating server will try again after a delay (15-30 minutes), and if sufficient time has elapsed, the email will be accepted. If the mail is from a spammer, it will probably not be retried since it goes through thousands of email addresses, and typically cannot afford the time delay to retry.
Grey-listing is a mechanism employed by various systems, such as email servers, to combat spam and other malicious activities. Unlike blacklisting, which outright blocks suspicious entities, Grey-listing temporarily defers incoming messages from unfamiliar sources and requires the sender to retry delivery later. This technique leverages the assumption that legitimate servers will follow the retry protocol while spammers and other malicious actors often do not.
Once we have grasped the fundamentals of Grey-listing, we can explore strategies and approaches to bypass its restrictions. By examining its inner workings, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and employing innovative techniques, it may be possible to navigate around Grey-listing mechanisms effectively. It is crucial, however, to approach this topic ethically and responsibly, ensuring that any bypass methods are implemented within legal and appropriate contexts.
What is Anti-Greylisting Technology
Anti-greylisting technology refers to mechanisms and methods designed to counteract or bypass the effects of Grey-listing. Grey-listing is a technique employed by email servers and other systems to combat spam and other malicious activities by temporarily deferring incoming messages from unfamiliar sources. However, some legitimate senders may encounter delays or difficulties when their messages are subjected to Grey-listing.
Anti-greylisting in the validation process is the technology of deliberate pauses between multiple validations try to simulate the behavior of a well-configured email server in order to prevent IP blocking.
How Anti-Greylisting Works
As mentioned above, greylisting is an anti-spam technology mail servers use to prevent spam. The receiving mail server tells the sender to please retry to send the email again in (X) minutes. A well-configured mail server will attempt to resend an email at different intervals until it's accepted or rejected by the receiving mail server. There are many types of greylisting, but the most common is time-based greylisting, as mentioned above.
Each mail server has a different time they greylist the sender for, normally between 1 and 30 minutes per email. DeBounce deploys breakthrough anti-grey-listing technology. When it encounters any greylisting, it will wait 30 minutes and retry to validate those specific emails. This reduces the amount of "Unknowns" received back. So, you wait a little longer for your results when validating them, but your results will be much better. It doesn't matter how many greylisted email addresses you upload, whether it's 1 or 100,000. The processing is only delayed by 30~60 minutes in total if you use it as a service for email verification. Email validation takes more time using anti-greylisting, but it's worth it.
To address these challenges, Anti-Greylisting technology aims to overcome or minimize the impact of Grey-listing measures. It typically involves implementing various strategies to ensure legitimate emails' successful and timely delivery. These strategies may include:
- Persistent Retries: Anti-greylisting technology may involve configuring email servers to make repeated delivery attempts at regular intervals until the recipient's server accepts the message. By persistently retrying, legitimate senders can overcome the temporary deferral imposed by Grey-listing.
- Whitelisting: Whitelisting involves pre-approving certain senders or domains deemed trustworthy. By adding trusted senders to a whitelist, their messages can bypass Grey-listing checks altogether, ensuring prompt delivery.
- Reputation-based Systems: Anti-greylisting technology may utilize reputation-based systems that assess the trustworthiness of senders based on their past behavior. If a sender has a positive reputation, their messages may be exempted from Grey-listing measures, expediting delivery.
- Grey-listing Mitigation Tools: Some software or tools are specifically designed to counteract Grey-listing. These tools may automatically handle the retry process, manage whitelists, or employ other techniques to minimize the impact of Grey-listing on legitimate email delivery.
It's worth noting that while Anti-Greylisting technology can help address legitimate email delivery issues caused by Grey-listing, it is important to use such technology responsibly and in compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
How to Prevent Grey-listing
Here are some straightforward precautions to help you avoid Grey-listing:
- Maintain a good sender and IP reputation: Ensure that your email sender and IP address have a positive reputation by adhering to email best practices, avoiding spamming activities, and resolving any issues promptly. A good reputation increases the chances of your emails bypassing Grey-listing measures.
- Use a reliable domain: Utilize a reputable and established domain for your email communications. Domains with a history of sending legitimate emails are less likely to be subjected to Grey-listing.
- Provide instant unsubscription option: Include a clear and easy-to-use unsubscribe option in your emails. This shows that you respect recipients' preferences and reduces the likelihood of your messages being flagged as spam.
- Use a real sender's name: When signing up for an email account or sending emails, use a legitimate, recognizable sender's name. This helps establish trust and credibility with recipients and reduces the chances of being flagged by Grey-listing systems.
- Avoid spammy words: Refrain from using words or phrases commonly associated with spam in your email subject lines and content. Words like "Buy," "Hurry," "Free," or excessive use of exclamation marks can trigger spam filters and increase the likelihood of Grey-listing.
- Format emails according to standards: Follow the HTML standards and RFC 5322 guidelines for formatting the heading and content of your emails. Compliance with these standards ensures that your messages are more likely to be accepted and delivered without triggering Grey-listing mechanisms.
By implementing these simple precautions, you can reduce the chances of your emails being subjected to Grey-listing and increase the likelihood of successful delivery to recipients' inboxes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the article has shed light on the concept of Anti-Greylisting technology and its role in mitigating the challenges posed by Grey-listing mechanisms. While effective in combating spam and malicious activities, Grey-listing can sometimes impede the delivery of legitimate emails. Anti-greylisting technology offers strategies and methods to overcome or minimize the impact of Grey-listing, ensuring that important messages reach their intended recipients in a timely manner.
By maintaining a good sender and IP reputation, using reliable domains, providing instant unsubscription options, employing real sender names, avoiding spammy words, and adhering to email formatting standards, individuals and organizations can enhance their chances of bypassing Grey-listing measures. When implemented responsibly and ethically, these simple precautions contribute to smoother email communication and help foster trust between senders and recipients.
It is important to note that while Anti-Greylisting technology provides valuable solutions, it should be used in compliance with legal and industry regulations. Respecting recipients' preferences, avoiding spamming practices, and upholding email best practices are essential for maintaining a positive sender reputation and ensuring the long-term effectiveness of Anti-Greylisting measures.




![Security Guide for Email Marketers [2025]](https://ik.imagekit.io/debounce/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/email-marketers-security-guide-300x139.png)
