There are certain best practices that every professional involved in email marketing knows. Things that most comprehensive guides detail, such as using email templates, setting up automated workflows, segmenting email lists, and testing email campaigns.
And then there are those unsung heroes that aren't as popular but play a pivotal role in your email marketing efforts. One of them is the return path email. No matter how well-thought-out your strategy is, the first thing you should ensure is that your emails end up in the right place.
This is where the return path comes into play. Our guide will explore the world of return-path-header, explaining what they are and discussing why they're important and how they work. As a bonus, we'll delve into the best practices to maximize the impact of a return path address, so you keep your emails out of the spam folder.
What Is a Return Path Email?
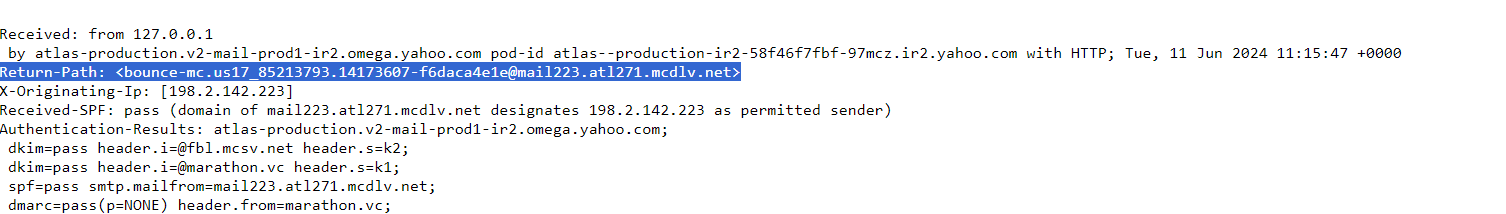
A return path email is a designated email address that communicates with SMTP servers, indicating where they should send bounced emails. Also called bounce address, reverse path, 5321-DE, or envelope from, the return path notifies senders about the delivery failure and the reason behind it.
While the return path is specified in the email header, it remains hidden from other parties. So, your subscribers won't be able to see the return-path-header unless they choose to display the original email header. Keep in mind that an email can have only one return path.

Now let's see what benefits you gain from setting up an email return path.
Why Is Return Path Email Important?
Email senders use return path email to monitor and analyze non-delivery receipts. By doing so, they can take corrective measures to strengthen their sender reputation and increase email deliverability rates. Here's how having a proper return-path-header helps you enhance your email campaigns:
- As an SMTP address, the return path helps email clients decide whether or not they must filter your emails. That way, they can verify your identity as a legitimate and credible sender—therefore, not a spammer.
- When a bounce occurs, email senders should know where to send the corresponding notification. By setting a return-path-header and monitoring non-delivery reports, you can detect and remove the addresses linked to bounces. This process simplifies maintaining a high-quality and clean email list and keeping crucial KPIs high.
- A well-configured return path is your safest bet at addressing bounced emails quickly. You can keep track of delivered and bounced emails and figure out why some of your messages fall into the second category. Basically, you get a roadmap for what you need to fix and how.
- Return path is directly linked to properly authenticating your emails according to DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) and SPF (Sender Policy Framework) protocols. Having a return-path-header in place helps you pass these authentication checks, thus verifying the legitimacy of your emails. Plus, you prevent phishing and spam attempts and build trust with your subscribers.
How does an Email Return Path Work?
Email return path is an essential tool in your marketing toolkit, especially if you send mass emails. Let’s say you want to send an email campaign announcing a seasonal sale to your entire email list—and that list includes thousands of recipients. While you don't want any emails to bounce, unfortunately, some of them will.
When email clients receive your emails, they try to verify your identity as a sender and ensure that no spam messages reach users’ inboxes. If, for some reason, your email goes into spam, the provider will send a bounce message to the return path address.
Basically, a failed delivery could occur due to a soft or hard bounce.
- Soft bounces occur when there's a temporary problem with the subscriber's inbox. The most common case is that it's full or there could be something wrong with one of your email files or attachments.
- Hard bounces result from a permanent issue related to the target email address itself. This means that it could be fake, outdated, or misspelled.
So, let’s say some email campaigns didn't make it to the subscribers’ inboxes. What's next? You'll need to find out why it happens. Once you determine the “why,” answering the “how to fix it” will be straightforward.
For example, if there's a soft bounce because of a file, you should consider resizing it or checking what's wrong. After addressing the issue, try to resend the campaign. Then, monitor the email address to see what happens. If it keeps bouncing, the wise thing to do is treat it like a hard bounce and remove the address from your list.
In the case of a hard bounce, you may have typed the address incorrectly. If you fill it in once more and it doesn't work, it's time to remove the corresponding contact from your database.
Keep in mind there's always a return path for every email you send, even if you do so through a free email address like a Gmail account. In that case, the bounce address will probably be the same as the sender address. Which brings us to a common question: is the return path header the same as the sender address?
Is the Return Path Email the Same as the Sender Address?
The short answer is that it depends on the email service provider. Most email marketing platforms let you send emails using their own domain names. This means that the return path email is different from the sender address. The logic behind this is that when sending thousands of emails, it's hard to deal with both sent and bounced emails in the same inbox.
Now, the right answer is that it should be. You see, if the bounce address differs from the sender, the bounce receipts go to a domain name that users don't have control over. As a result, they can't monitor the data as efficiently and quickly as they would using the same domain name. As opposed to when the return path matches the sender address. In which case, you have complete control over your records and can take corrective actions immediately.
Why Should You Create a Custom Return Path?
So, it's common for email services not to give you the option to have the same domain name as the bounce address and the sender. Even so, it's wise to create a custom return path email. The reason for setting a customized return path has to do with email authentication systems.
For instance, one of the things that DMARC checks is whether your sender name and return path name are aligned. If they match, your emails will probably pass the SPF alignment set by DMARC.
This may be just an aspect of how authentication protocols check your sender reputation. But the more consistent your messages, the greater the chances of your emails getting through the filters each email client uses and making it to inboxes. Having a clear return-path-header will not only protect your subscribers but also increase your deliverability.
Some email marketing services let you set up a custom domain name. Besides creating a customized return path domain, it includes verifying it through the DNS record. However, each email tool has its own settings, and you'll have to go through its help center to find the setup instructions. Alternatively, you can contact the customer service team to ask if they provide such a setting and they should walk you through the configuration process.
What a handful of tools like Moosend do differently is that they automatically set the return-path-header to be the same as the sender address. That way, users can display and manage the bounced messages without intermediaries. So, let's say a Moosend user sends emails from [email protected]. The return path email would be [email protected], and not a Moosend-owned address That way, the sender monitors each non-delivery notification as soon as it comes in.
How Can You Display the Return Path Address in Different Email Clients?
If you want to display the reverse path email in different email clients, there are certain steps you should take. Here's how you can do this in the most popular email providers:
How to Display the Return Path in Gmail
If you want to view the return path of an email in Gmail, open the email and click on the burger menu. From the options appearing, tap on Show Original.

Once the new tab opens, scroll down until you find the Return path. Alternatively, use the search option to detect it.
How to Display the Return Path in Microsoft Outlook
In Outlook, you should right-click on the email you want to display the reverse path for, and then select View page source.
As in Gmail, you can manually find the Return path option or use the search box.
How to Display the Return Path in Yahoo
Open the email you need to view the return path for and click on the burger menu. Then, tap on the View raw message option.
A tab will open, and you should look for the return path address by scrolling down the text. Again, you could do so through the search option, too.
How to Display the Return Path in Apple Mail
If you own an Apple Mail account, there's also an easy way to display the return-path-header for every email. Once you're inside the email, tap on the View tab and then on Messages. Lastly, click on All headers.
When the right reading pane opens, scroll down to find the word ‘Return path’.
We've covered all the basics of the reverse path email. Now, how can you enhance its impact and refine your overall email marketing strategy?
4 Best Practices to Make the Most of Your Return Path Email
With a strong return path, you can safeguard your sender reputation and contact the majority of your subscribers effectively. The following practices will help you support your bounce address and further improve your email deliverability.
Choose a Reliable Email Tool
Before picking an email service provider, you should spend some time reading user reviews and exploring different options. Focus on each email tool's return path management, going through their documentation to see if there's an option to create a custom reverse path email. Plus, research their practices regarding email authentication.
Remember to check reports for their email deliverability rates, too. You might do everything right, but investing in a platform with high deliverability ensures you get your emails past email clients. You must choose a reliable and robust ESP in terms of contact management and email analytics so you can optimize your emails based on audience data. Last but not least, make sure you test the platform's capabilities through a free version or trial to check if it matches your business requirements.
Use Email Authentication Protocols
Email authentication consists of a list of activities designed to confirm and validate your sender identity. Authentication methods include protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify that the email is coming from a trusted sender instead of a spamming, spoofing, or phishing attack. There are several benefits when you use these methods to authenticate your emails. Let's review them:
- SPF verifies that the email content is sent by a trustworthy domain, and that the sender is qualified to send emails on behalf of it.
- DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) serves as a digital signature, telling mailbox providers that your email was authorized by you, the rightful domain owner. DKIM uses a public and a private key to ensure there are no impostors involved in your messages.
- DMARC builds on SPF and DKIM. This mechanism allows domain owners to define how emails that fail authentication checks should be handled. That way, they prevent unauthorized parties from using your domain.
Fortunately, reliable email marketing software implements all the protocols needed. They do the heavy lifting for you, ensuring you have a great sender reputation and helping you reach your subscribers with safety and security.
Sanitize your Email List
A good sender reputation and excellent deliverability rates go hand in hand with maintaining a healthy email list. Delivering email content to inactive recipients or fake email addresses could lead to high bounce rates and spam complaints, thus decreasing your sender score.
Cleaning your mailing list starts with removing invalid or duplicate email addresses and unengaged or inactive contacts. Also, it should include identifying and removing addresses connected to hard bounces. To avoid adding invalid addresses to your list, always use a double opt-in process for email signups so recipients can confirm their subscription through their account.
You can set up automated processes that ensure list hygiene to save time. For instance, send automated re-engagement email campaigns to recipients who haven't interacted with your emails over a specific period. If they remain uninterested, remove them from your database.
Track and Analyze your Sender's Reputation
Monitoring your sender's reputation is essential for maintaining strong deliverability. Factors like too many spam complaints or high bounce rates may affect your sender's reputation. This measure reflects how email clients view your sending practices. So, tracking it at regular intervals helps you act as quickly as possible and take corrective actions to improve it.
If you notice your sender's reputation dropping, first you should identify what's causing this. Some of the most common reasons include spam complaints, bounce and unsubscribe rates, sending volume and frequency, and email engagement. It all comes down to your email campaign performance, and how you can use the data you collect to optimize future emails.
As with every marketing effort, email comes with its challenges. One of them includes monitoring and dealing with email bounces. Having a well-configured email return path acts as a protection mechanism for your emails to land safely in recipient inboxes.
Your return-path-header plays an important role in keeping your email deliverability high, your bounce rates low, and your sender reputation intact. Therefore, you must invest in an email marketing platform that lets you customize your return path. Also, make sure it offers all the tools and features to maximize its impact.
Remember that it will show you the way to respond to email errors promptly, bringing improved email performance and more delivered emails.






![Security Guide for Email Marketers [2025]](https://ik.imagekit.io/debounce/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/email-marketers-security-guide-300x139.png)